GIA Certification
Diamond Certification & Reports

For more than 50 years, fine jewellers everywhere have considered the GIA Diamond Grading Report the premier credential of a diamond’s authenticity and quality. A GIA Gem Laboratory is the ultimate sign of credibility for loose diamonds and gives you 100% clarification of its technical data.GIA is a USA based independent commercial grading institute, and is a non-profit organisation.
GIA Diamond Grading Report
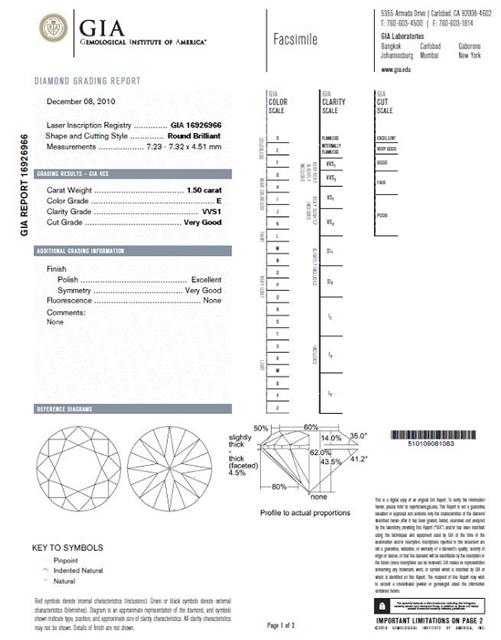
The GIA Diamond Grading Report includes an assessment of a diamond’s 4’C’s – colour, clarity, cut, and carat weight – along with a plotted diagram of its clarity characteristics and a graphic representation of the diamond’s proportions.
For standard round brilliant cut diamonds falling in the D-Z colour range, the report also includes a GIA Cut grade.
The GIA Laboratory issues diamond grading reports for loose, natural diamonds in the D-Z colour range that weigh 0.15 carats or more.
GIA Diamond Grading Reports are not issued for synthetics, simulants, mounted diamonds or those that have undergone unstable treatments, such as fracture filling or coating.
And while reports may be issued for diamonds that have been laser drilled or HPHT processed, these stable treatments are prominently disclosed on the report.
ANATOMY OF A GIA REPORT
GIA Diamond Dossier ®

The GIA Diamond Dossier offers the same grading information as the GIA Diamond Grading Report but without the plotted diagram.
As an added security feature, the Dossier service includes a microscopic laser inscription of the report number on the Diamond’s girdle.
The GIA Laboratory issues the Diamond Dossier for loose, natural diamonds between 0.15 and 1.99 carats, in the D-Z colour range.
The Diamond Dossier is not issued for synthetics, simulants, mounted diamonds, diamonds that have undergone unstable treatments such as fracture filling or coating, or those that have been HPHT processed.
Any evidence of other treatment is prominently disclosed in the report
ANATOMY OF DOSSIER REPORT
Laser Inscription
Upon request, a diamond can be microscopically inscribed on its girdle with its unique GIA Report Number (referred to as the GIA Inscription Registry), a personal message, or any other text, symbols or logos. The GIA Inscription Registry is included with the Diamond Dossier® service and all synthetic diamond report services. A laser inscription allows for easy identification of a diamond, a way to personalize the diamond, or serves as a form of branding for the diamond manufacturer or retailer.


How GIA Grades Diamonds
People from all over the world send their diamonds to the sixteen GIA laboratories positioned around the world for grading and analysis. Our clients put their business in our hands and their trust in our expertise – and we are extremely careful with both.
Belgium – GIA LabDirect Consolidators – Belgium – Lea Retter Rapaport – GIA Israel Laboratory
Israel – GIA LabDirect Consolidators – Israel – Joshua Kersh Rapaport – GIA India Laboratory Pvt. Ltd.
India – GIA LabDirect Consolidator – GIA Laboratory Service Center Dubai – GIA Thailand
GIA Hong Kong Laboratory Limited – GIA Tokyo Godo Kaisha
Objectivity and independence are the hallmarks of all GIA reports and services, and GIA has elaborate processes in place to ensure a diamond’s anonymity through the grading process. Upon arrival to the laboratory, every diamond is placed in a custom designed, transparent storage case, and all references to its owner are removed or concealed. It is assigned a bar-coded label with a unique internal identification number that is used to track it throughout the process. Furthermore, client information is masked within the software diamond graders use to enter their assessments. We ask that our clients assist us in this process by submitting items in parcel papers free of information that identifies them as the client or refers to grading information.
Weights and Measures
Diamonds are weighed with an electronic micro-balance that captures their weight to the fifth decimal place. An optical measuring device determines their proportions, measurements, and facet angles.
Grading Colour
Since light source and background can have a significant impact on the appearance of colour, the diamond’s colour is graded in a standardised viewing environment. Colour graders submit their independent opinions into the system. During this phase, graders are not privy to colour opinions entered previously. The colour grade is determined when there are sufficient agreeing opinions
Clarityis graded with 10x magnification under standard viewing conditions. The preliminary grader carefully examines the diamond to locate clarity/finish characteristics and evidence of any diamond treatments, such as fracture filling or laser drilling.
The preliminary grader assigns an opinion of the diamond’s clarity, polish and symmetry, then plots the clarity characteristics on a diagram most representative of the diamond’s shape and faceting style, which is selected from a database of hundreds of digitally stored diagrams. During this step, the grader verifies all previously captured weight and measurement data and assigns written descriptions of the diamond’s culet and girdle thickness. For a round brilliant cut diamond, this measurement data, along with polish and symmetry assessments, is used to determine its GIA Cut Grade. Additional steps are also taken during this grading process, and all others, to check and double check for indicators of known diamond treatments and synthetics.
A second grader then carefully and thoroughly examines the diamond to locate and identify clarity/finish characteristics and, again, the presence of any diamond treatments. This grader performs all the same grading steps done by the previous grader and then enters an independent opinion on clarity/polish/symmetry.
Depending on the diamond’s weight, quality, and the agreement of grading opinions, additional quality assurance process steps are also performed. More experienced staff gemologists may review all of the previous grading information and render independent clarity/polish/symmetry opinions. Grading results are finalised once there are sufficient agreeing opinions.
Grading Cut 
GIA provides a cut quality grade only for standard round brilliant diamonds that fall in the GIA D-to-Z colour range.
After the colour and clarity grading process, the diamond’s proportions (measurements and facet angles), along with polish and symmetry descriptions, are used to determine its GIA Cut Grade. A diamond’s brightness, fire, scintillation (sparkle and pattern), weight ratio, and durability, as well as polish and symmetry, are all considered within this final assessment of cut quality.
Inspection, Care and Handling Procedures
At every step of the grading process, special inspection, care, and handling procedures are in place to protect a diamond’s identity and ensure the diamond is managed with the utmost care.
GIA’s Inventory Control Department serves as the hub for laboratory operations. Between grading process steps, a diamond is distributed from and returned to this department, ensuring that the distribution of diamonds to graders is completely random. This is just one of several critical measures in an independent and impartial grading process.
Every diamond is tracked electronically so that the laboratory can pinpoint its exact location at any time, and review each step during the grading process. With thousands of diamonds, and hundreds of diamond graders, the routing and tracking of the GIA laboratory’s inventory requires a highly trained and alert staff, combined with the best support technology can offer.

